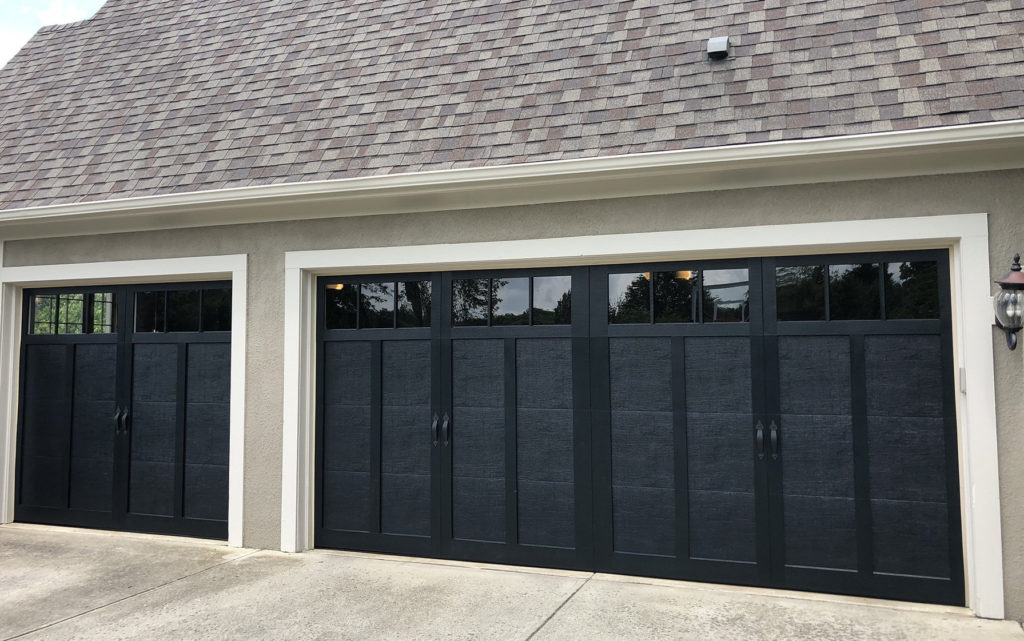
Garage door are among the most essential components of a home. While often overlooked, they serve as the primary entry and exit point for vehicles, enhance the security of your property, and add aesthetic value to your home. Understanding its anatomy not only helps in troubleshooting minor problems but also ensures you can maintain it properly for long-lasting performance.
Whether you’re a homeowner curious about the door’s inner workings or planning a repair, this guide will provide a detailed look at the essential components and how they work together to keep your home secure and functional.

Content
Key Components of a Garage Door
A garage door is more than just a large panel that moves up and down. It is a sophisticated system of several interconnected components that must work together to ensure smooth operation. Here’s a breakdown of the most important parts:
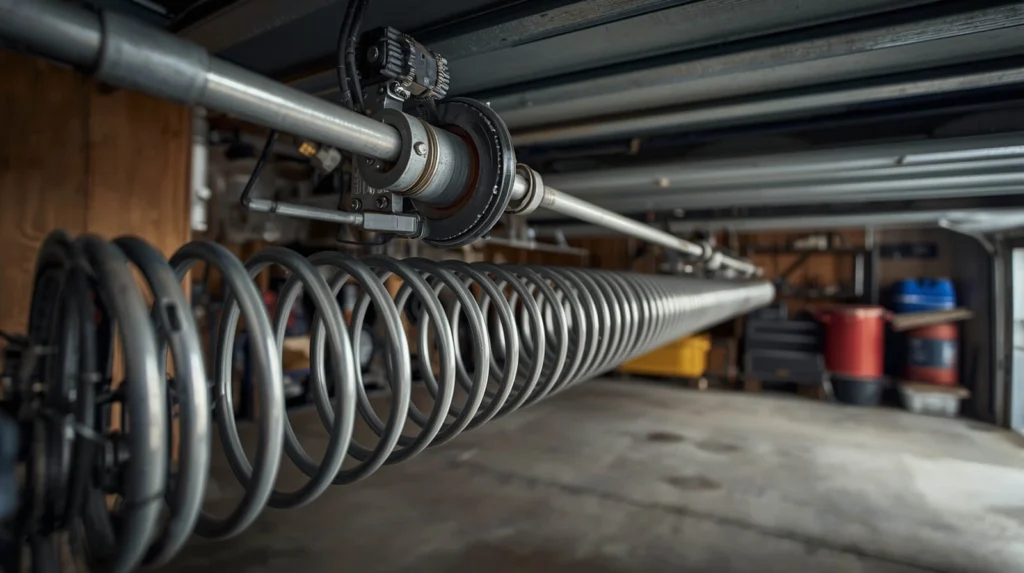
1. Springs: The Power Behind the Door
Springs are one of the most critical components of a garage door. They counterbalance the weight of the door, making it possible to open and close the door manually or automatically without straining the motor.
There are two main types of springs used in garage doors:
Torsion Springs:

Mounted above the opening, torsion springs are the most common choice for residential doors. They are highly durable, provide precise tension control, and are safer compared to other types of springs. Torsion springs typically last up to 10 years, depending on usage.
Extension Springs:
These are located on either side of the door tracks. They extend and contract to lift and lower the door. While slightly less durable than torsion springs, extension springs can last up to 7 years.
2. Cables and Hinges: Ensuring Smooth Motion
Cables and hinges are vital to the safe and precise operation of your garage door.
- Cables: Made of high-strength braided steel, these cables work alongside springs to lift and lower the door. They carry the weight of the door and should always be free from fraying or damage.
- Hinges: Hinges connect the door panels and allow them to bend and move along the tracks. Larger or heavier doors usually require additional hinges for balanced and smooth operation.
3. Tracks and Rollers: Guiding the Door
The tracks and rollers form the pathway along which the door moves.
- Tracks: Typically made of galvanized steel, tracks are mounted on both sides of the door and ensure the panels move straight and safely.
- Rollers: Small wheels attached to the door that glide along the tracks, rollers are essential for smooth operation. Quality rollers reduce noise and wear on other components.
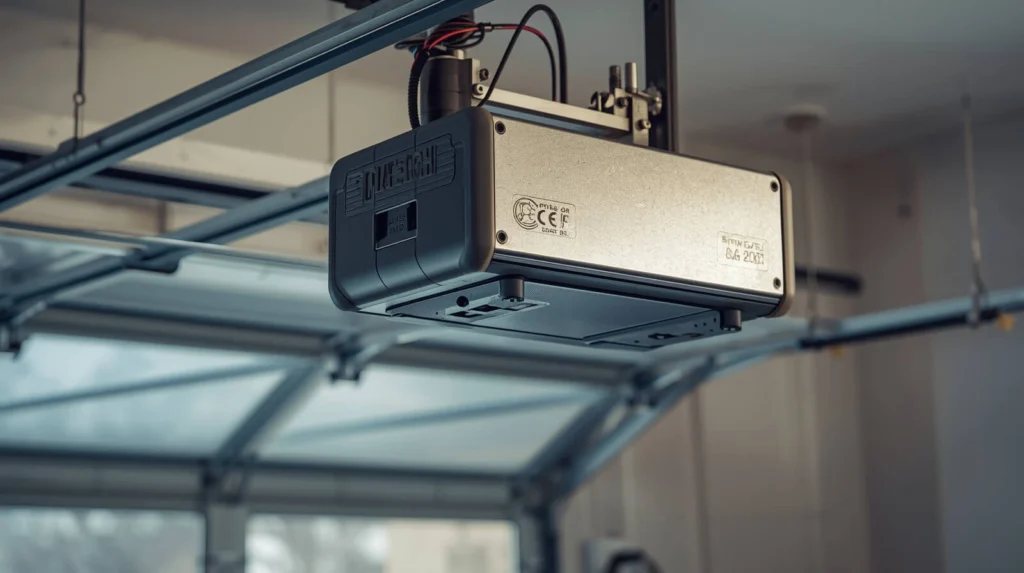
4. Garage Door Opener: The Automated Mechanism

Most modern doors come equipped with a motorized opener, making opening and closing effortless. These openers are powered by electricity and operate via a chain, belt, or screw drive.
- Chain Drive Openers: Durable and affordable, chain drives are slightly noisier than other types.
- Belt Drive Openers: Quieter and smoother, these are ideal for homes where the garage is attached to living spaces.
- Screw Drive Openers: Require less maintenance and provide consistent performance, though they are a bit noisier than belt drives.
Openers often include safety features such as auto-reverse sensors, manual release handles, and smart connectivity for remote operation.
5. Safety Sensors: Protecting Your Home and Family
Safety sensors are small but crucial components of your garage door system. Installed near the bottom of the door tracks, these sensors detect obstacles and prevent the door from closing on objects, pets, or people.
Many homeowners overlook safety sensors during maintenance, but they are required by law in most regions for automatic doors. Ensuring these sensors are clean, aligned, and functioning is critical for household safety.
6. Reinforced Struts: Supporting Large Doors
Reinforced struts are horizontal supports that strengthen larger doors and prevent bowing. They are particularly important for double or triple-car doors and help maintain structural integrity over time.
Types of Garage Doors
Understanding the type of garage door you have can help you maintain it better. There are several common types:
Sectional Doors:
Made of multiple horizontal panels that bend as the door opens. Sectional doors are popular due to their durability and smooth operation.
Roll-Up Doors:
Ideal for commercial spaces, these doors roll into a compact coil above the opening.
Slide-to-the-Side Doors:

Move horizontally along a track and are useful when ceiling space is limited.
Side-Hinged Doors:
Swings open like traditional doors and are often used for smaller garages or barns.
Tilt-Up Canopy Doors:
Single solid panels that tilt outward when opened.
Garage Door Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance ensures your garage door operates safely and lasts longer. Here are some essential tips:
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Use door lubricant on hinges, rollers, tracks, and springs at least twice a year.
- Check Cables and Springs: Look for signs of wear, fraying, or rust. Replace any damaged parts promptly.
- Test Auto-Reverse Function: Place an object in the doorway and close the door. It should reverse immediately.
- Inspect Tracks and Rollers: Clean tracks to remove debris and check rollers for smooth motion.
- Balance the Door: Disconnect the opener and lift the door manually. A balanced door should stay in place when lifted halfway.
Signs Your Door Needs Repair
Even with proper maintenance, wear and tear can occur. Watch out for these warning signs:
- Strange Noises: Grinding, squeaking, or popping sounds indicate worn rollers or hardware.
- Slow or Uneven Operation: Could be due to spring tension issues or worn-out opener components.
- Door Not Closing Properly: Safety sensors, tracks, or cables may be misaligned.
- Sagging Panels or Bent Tracks: Signs of structural issues requiring immediate attention.
Advantages of Keeping Your Door Well-Maintained
Maintaining your door goes beyond functionality—it impacts your home in several ways:
- Enhanced Security: A properly functioning door prevents unauthorized access.
- Energy Efficiency: Insulated doors reduce heat loss and save on energy bills.
- Curb Appeal: A clean, well-maintained door improves your home’s appearance and value.
- Longevity: Routine maintenance extends the lifespan of all components, saving you money over time.
Choosing the Right Door Services
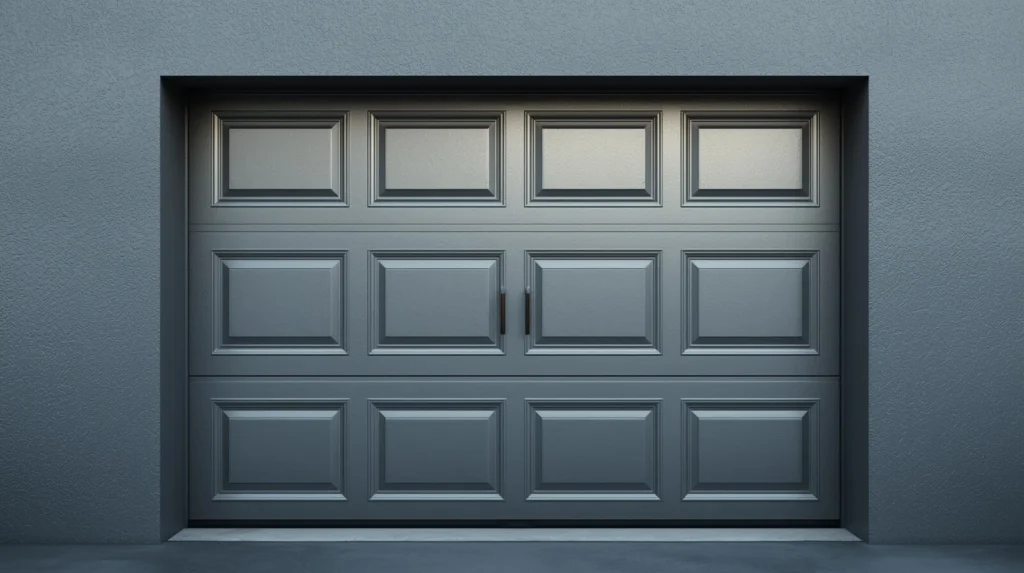

Hiring professional technicians for Glass Garage Doors ensures safe, reliable, and long-lasting repairs or installations. When choosing a service provider, consider:
- Experience and expertise with different door types
- Licensing and insurance coverage
- Availability of emergency services
- Customer reviews and warranty options
FAQs
How big is a 4-car garage in meters?
A 4-car garage typically measures around 12–15 meters wide and 6–7 meters deep, depending on layout and design.
Why are garage doors so expensive?
High costs come from quality materials, durable hardware, insulation, and professional installation.
How much does a separate 2-car garage cost?
A detached 2-car garage usually costs between $20,000–$50,000, depending on size, materials, and features.
How much does an electric garage door cost?
Electric doors range from $1,000–$4,000 for standard residential models, with prices increasing for premium options.

Meet Jack, our garage guru. With a wrench in one hand and a can-do attitude in the other, he’s your go-to expert for all things repair and replacement.